Context and Problem:
Many Cloud Solutions involve running tasks that invoke services, if the service is subjected to intermittent heavy loads, we will end up in performance degradation and availability issues. This leads to tasks getting timed out or the service getting failed.
A service can be invoked by multiple tasks concurrently and it is difficult to predict the volume of requests to the services at any time. Because of this reason, services might not respond to the tasks in a timely manner and also lead to service failures due to contention issues. Task and Service are tightly coupled in this case.
Solution :
In order to overcome such issues, you need to decouple the task and service to run asynchronously and the answer for this is Queue-Based Load Leveling Pattern. Implementing this design pattern introduces a queue that acts as a buffer between the task and the service in order to smoothen the intermittent heavy loads thereby minimizing the impact of the peak in demand on the Availability and Responsiveness of the Service.
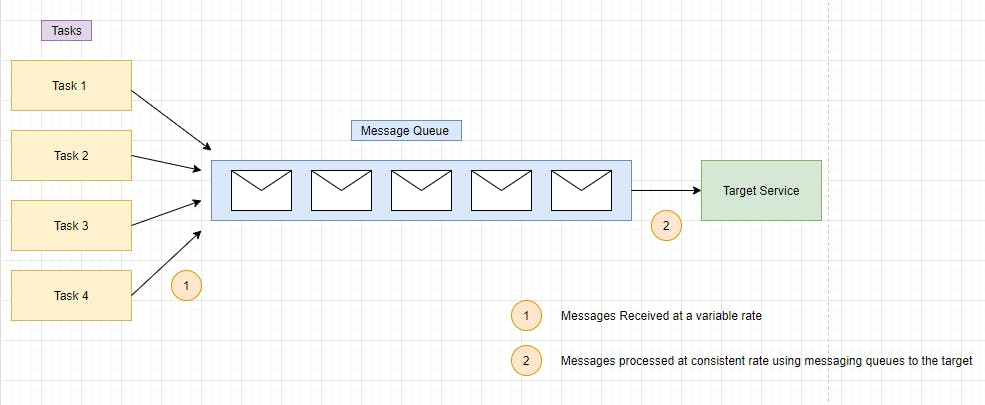
Benefits :
- Messages processed via queue remains in the queue until it is processed offsetting the impact of downstream load.
- Queue Mechanism also ensures if there is a system outage i.e. Downstream systems like API or Database are down, a message will be still be handled. It would remain in the queue and would be processed back once the system is online. This helps maximize availability because it negates the impact of delays arising in downstream systems.
- Helps maximize Scalability because the number of queues and number of services can be varied on demand.
- Some Services Implement throttling due to which systems get overwhelmed and fail once the traffic reaches the threshold. We can implement load-leveling with these services to ensure the threshold is not reached.
Issues and Considerations :
- Messaging Queues are one way mechanism , so if you source task is expecting a response back from the service , it is necessary to implement a mechanism that the service can be used to send a response . We can use Asynchronous Messaging Primer pattern to overcome this problem.
- Be careful while implementing autoscaling on the target system which receives the request from the Queue because it negates the effect of using the queue to level the load on the target if not managed properly.
- Make sure you test the system under the load to ensure that you arrive at an optimal number of queues and services instances to handle the message load.
Scenario to implement this pattern :
- This pattern is applicable to any applications that uses services that subject to overloading.
- This pattern is not useful if the service expects a response with minimal latency.
Implementation of the Pattern in Azure in different Scenarios :
Problem :
A web app writing data to the external data store. If the number of web app instances run concurrently the data store might not respond to requests quickly enough causing requests to timeout, throttle, or otherwise getting failed.
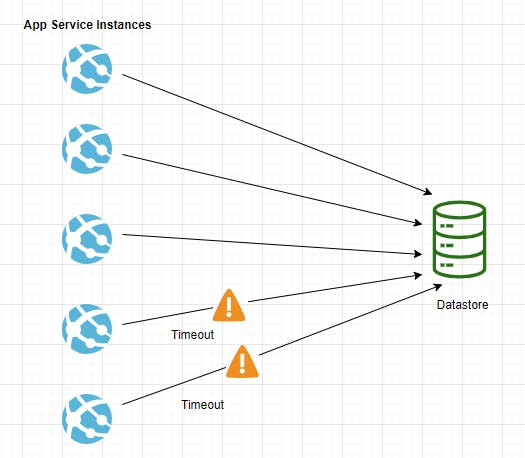
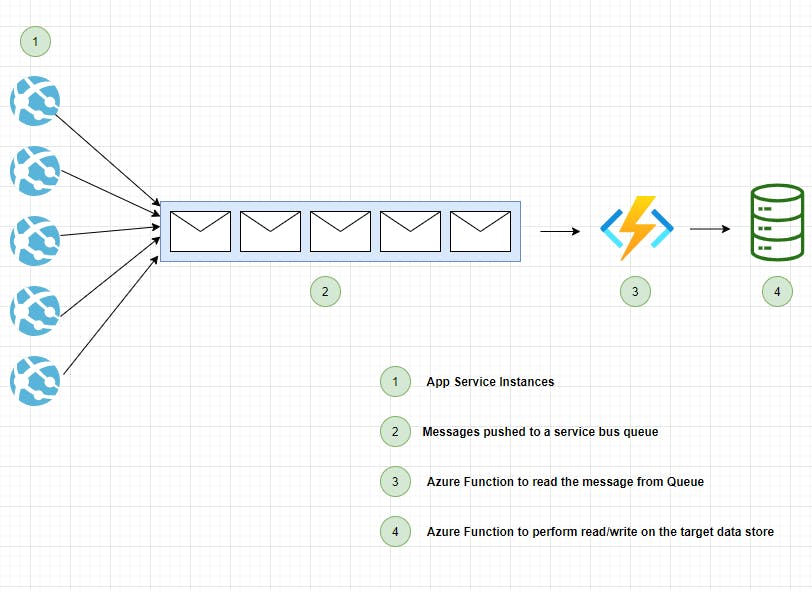
Solution :
To resolve the above problem, we can use this queue-based load leveling pattern by introducing the messaging queue to level the load between the application instances and the data store. Azure Function App reads the messages from the queue and performs read/write to the data store. Application logic written in the function app can control the rate at which the requests are being sent to the data store to prevent the store from being overwhelmed.
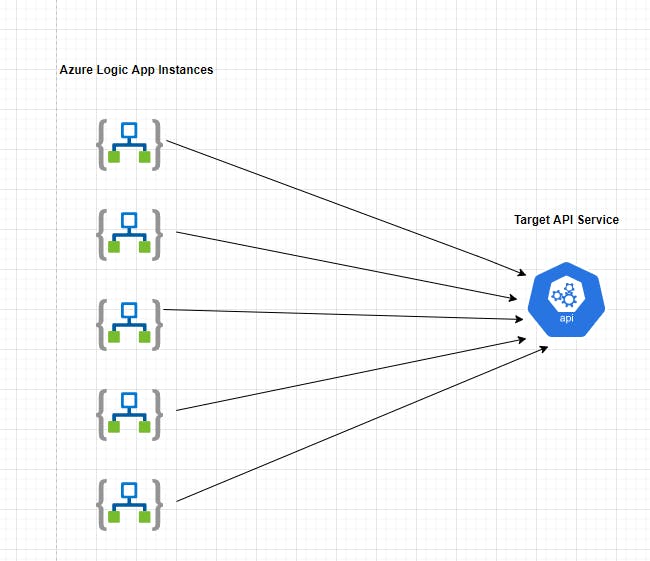
Problem :
An Azure Logic app / Function app trying to invoke an API which is a downstream system directly might come across scenarios where the API is down for some period of time or API is throttled. In such scenarios, it becomes very difficult to handle and process the message to the target system. Ultimately it affects the overall availability of the solution as we are not able to handle the downtime situation gracefully.
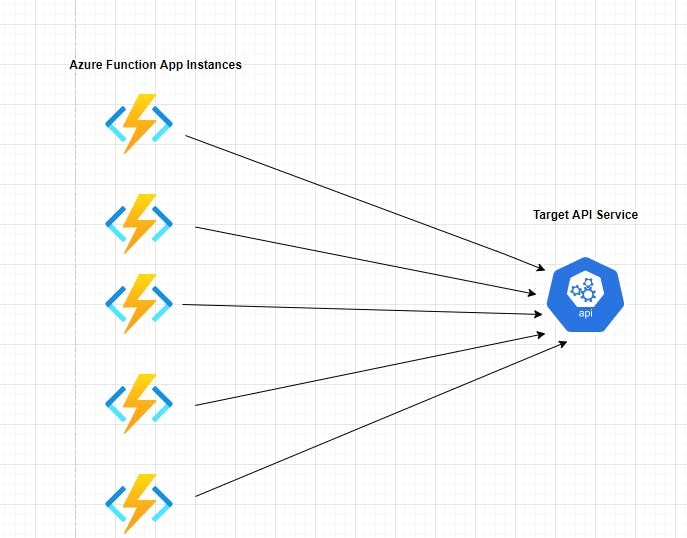
Solution :
To overcome the above problem, introduce a messaging layer to decouple the target from the source and at the same, the solution becomes more robust as the messaging queues level the load between the azure function/azure logic app and the target API. We introduce one more logic app/function app to poll the message from the queue and make a call to the Target API. With this approach, we can reduce the load on the target API during a high volume of traffic, and at the same time, we gracefully handle the messages while the target API is down as the message remains on the queue so that we can push the messages to the API once it is up and running.
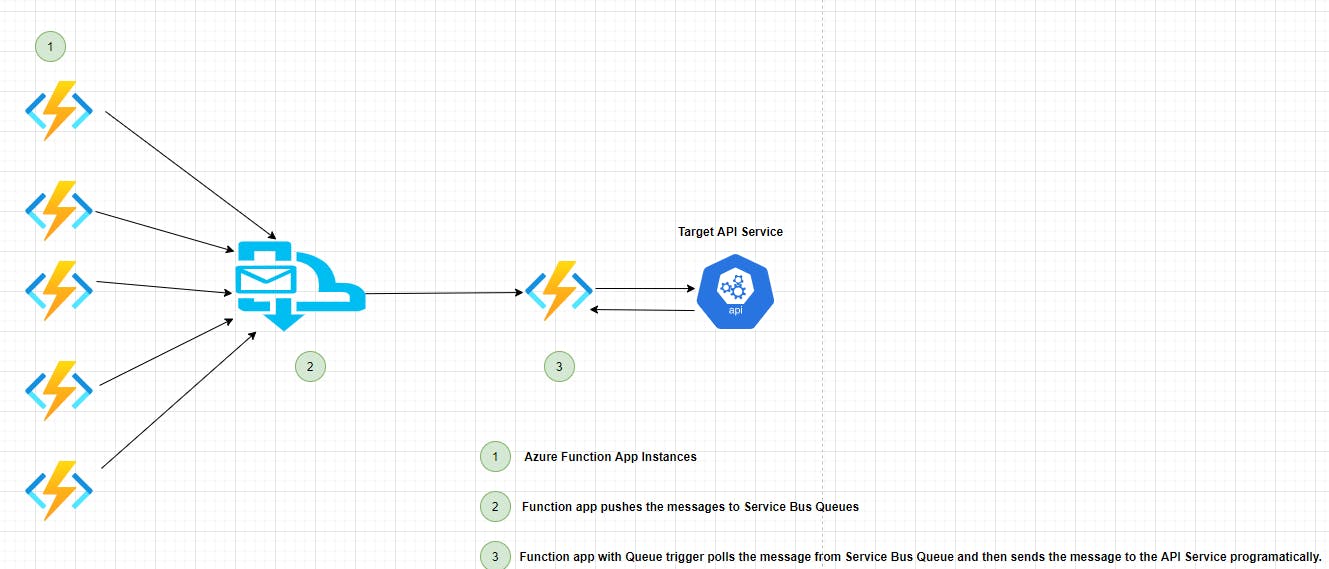
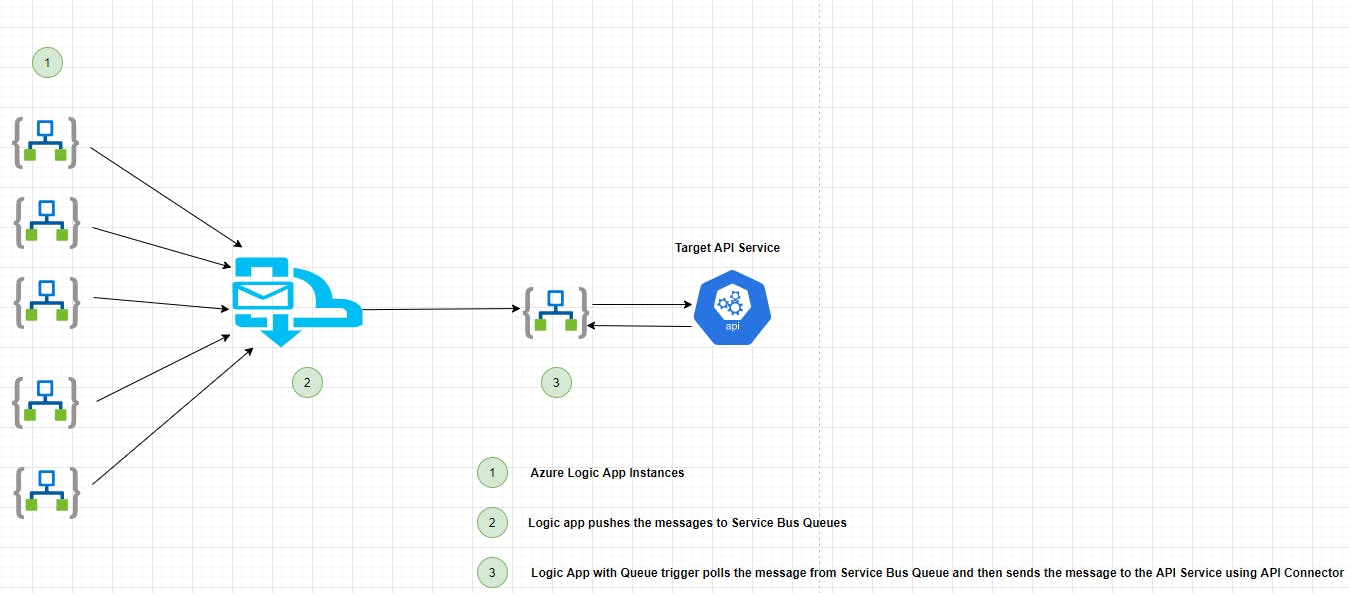
References :
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/architecture/patterns/queue-based-load-leveling

